What is Business Strategy?
A business strategy comprises decisions and actions guiding an organization toward long-term goals. Achieving a competitive advantage, maximizing performance, and ensuring success involves planning and executing initiatives. Elements like market positioning, resource allocation, innovation, and risk management are integral. Aligning strengths with external opportunities while addressing weaknesses and threats defines strategic adaptation. A clearly defined Business Strategy Examples serves as a decision-making roadmap, fostering adaptability to changing circumstances, promoting sustainable growth, and building resilience.
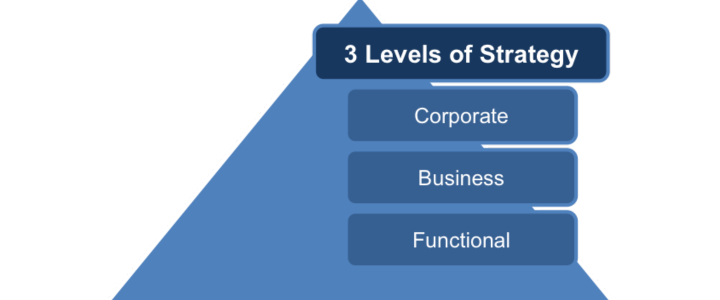
There are a variety of levels of business strategy.
Business strategy operates at various levels within an organization, each serving distinct purposes. The three primary levels of business strategy are:
Corporate Level Strategy:
- Focus: Concerned with the overall scope and direction of the entire organization.
- Key Decisions: Involves decisions related to the portfolio of businesses, mergers and acquisitions, diversification, and resource allocation among different business units.
- Example: A conglomerate deciding to enter new industries or divest from existing ones.
Business Unit Level Strategy:
- Focus: Concentrates on how individual business units within the organization will compete in their respective markets.
- Key Decisions: Involves market positioning, competitive advantage, and resource allocation specific to a particular business segment.
- Example: A business unit adopting a cost leadership strategy to become the low-cost producer in its industry.
Functional Level Strategy:
- Focus: Concerned with how each functional area (marketing, finance, operations, etc.) can contribute to the overall business unit strategy.
- Key Decisions: Involves decisions related to specific functions such as marketing campaigns, production processes, and financial management.
- Example: The marketing department implementing a targeted advertising campaign to support the business unit’s strategy.
These levels are interconnected, with corporate-level decisions influencing business unit strategies, and functional strategies supporting the achievement of broader business goals. A cohesive alignment of strategies at all levels is crucial for organizational success.
Factors That Are Crucial to a Business Strategy
A robust business strategy encompasses several key aspects essential for guiding an organization toward its goals and ensuring sustainable success:
Clear Vision and Mission:
- Articulating a concise and inspiring vision and mission provides the foundation for the strategy, defining the organization’s purpose and aspirations.
SWOT Analysis:
- Conducting a thorough analysis of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats helps identify internal capabilities and external factors influencing strategic decisions.
Goals and Objectives:
- Establishing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals ensures a focused and quantifiable approach to strategy execution.
Market Positioning:
- Defining how the organization wants to be perceived in the market relative to competitors is crucial for creating a distinctive and competitive market position.
Competitive Advantage:
- Identifying and leveraging unique strengths or capabilities that provide a competitive edge in the market is fundamental to sustained success.
Resource Allocation:
- Efficiently allocating resources, including financial, human, and technological, ensures that the organization can implement its strategy effectively.
Innovation and Adaptability:
- Integrating innovation into the strategy and fostering adaptability to changes in the business environment enhances the organization’s resilience and responsiveness.
Risk Management:
- Assessing and proactively addressing potential risks and uncertainties helps mitigate challenges and enhances the organization’s ability to navigate uncertainties.
Stakeholder Engagement:
- Recognizing and incorporating the interests of key stakeholders, including customers, employees, investors, and communities, contributes to a strategy’s success.
Monitoring and Evaluation:
- Implementing mechanisms to monitor progress, gather feedback, and evaluate performance against strategic objectives facilitates ongoing refinement and adjustment.
Communication and Alignment:
- Effectively communicating the strategy throughout the organization and ensuring alignment at all levels fosters a shared understanding and commitment to strategic goals.
A well-crafted business strategy integrates these aspects cohesively, providing a roadmap for the organization’s growth, competitiveness, and long-term viability.
five elements of business strategy with examples
Cost Leadership:
- Example: Walmart is a prime example of cost leadership. By focusing on operational efficiency, supply chain optimization, and cost minimization, Walmart offers a wide range of products at competitive prices.
Differentiation:
- Example: Apple’s differentiation strategy is evident in its premium products with unique design, advanced technology, and a strong emphasis on user experience, setting Apple apart in the consumer electronics market.
Focus or Niche Strategy:
- Example: Tesla employs a focus strategy by targeting the niche market of electric vehicles. Tesla’s innovation and emphasis on sustainability have established it as a leader in this specialized market segment.
Innovation Strategy:
- Example: Google’s innovation strategy is reflected in its constant development of new products and services. The introduction of Google Maps, Gmail, and Google Drive showcases its commitment to innovation in the tech industry.
E-commerce and Digital Transformation:
- Example: Amazon’s business strategy revolves around leveraging e-commerce and Digital Marketing. With a vast online marketplace, efficient logistics, and diverse product offerings, Amazon has transformed the retail landscape.
These examples illustrate how companies strategically position themselves in the market, whether through cost leadership, differentiation, focus on niche markets, innovation, or leveraging digital transformation for a competitive advantage.
Why is a Business Strategy Important?
A well-crafted business strategy is indispensable for the success and longevity of any organization. Serving as a roadmap, it guides decision-makers in prioritizing tasks and allocating resources efficiently, fostering a clear direction and focus. By differentiating the business from competitors and positioning it strategically in the market, a robust strategy creates a competitive advantage. Furthermore, it optimizes resource allocation, enabling effective risk management and adaptability to changing market conditions. In the long term, a sound strategy ensures sustainability, boosts stakeholder confidence, and provides a basis for measuring success through defined performance metrics. Additionally, it serves as a powerful communication tool, aligning the efforts of employees with the organization’s vision and fostering a sense of purpose. Ultimately, a well-defined business strategy is a dynamic framework that facilitates continuous improvement and adaptation in the ever-evolving business landscape.
Assessing the Effectiveness of a Business Strategy
Measuring the success of a business strategy involves evaluating various key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics that align with the strategic objectives. Here are some commonly used approaches and metrics for assessing the effectiveness of a business strategy:
Financial Metrics:
- Revenue Growth: An increase in revenue compared to previous periods or industry benchmarks.
- Profitability: Assess the net profit margin and return on investment (ROI) to ensure that the strategy is contributing to financial health.
Customer Metrics:
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: Surveys, feedback, and customer retention rates can gauge how well the strategy meets customer expectations.
- Market Share: An increase in market share indicates the strategy’s success in gaining a larger portion of the market.
Operational Metrics:
- Efficiency Improvements: Evaluate operational efficiency through metrics such as cost per unit, production cycle times, or resource utilization.
- Quality Metrics: Assess the quality of products or services to ensure they meet or exceed customer expectations.
Employee Engagement:
- Employee Satisfaction and Productivity: Measure employee satisfaction, retention rates, and productivity levels to gauge the impact of the strategy on the workforce.
- Skill Development: Evaluate whether the strategy is contributing to the development of employee skills and capabilities.
Innovation and Adaptability:
- New Product or Service Introductions: Monitor the success of new offerings and innovations resulting from the strategy.
- Adaptability: Assess the organization’s ability to adapt to changing market conditions and evolving customer needs.
Strategic Goal Achievement:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define and track KPIs that directly align with the strategic goals outlined in the business strategy.
- Benchmarking: Compare the organization’s performance against industry benchmarks and competitors.
Risk Management:
- Identification and Mitigation of Risks: Evaluate how well the strategy anticipates and addresses potential risks to the business.
- Resilience: Measure the organization’s ability to withstand external shocks or challenges.
Stakeholder Perception:
- Brand Image: Assess changes in brand perception and reputation among customers, investors, and other stakeholders.
- Communication Effectiveness: Evaluate how well the strategy is communicated and understood by internal and external stakeholders.
Technology and Data Analytics:
- Utilization of Technology: Measure the adoption and effectiveness of technology solutions in supporting the strategy.
- Data-Driven Insights: Leverage data analytics to gain insights into performance trends and areas for improvement.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting these metrics in light of changing circumstances ensures that the measurement of success remains dynamic and aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives. It’s essential to establish a comprehensive evaluation framework that captures the multifaceted aspects of business strategy success.
Conclusion
Webtoils stands as a prime example showcasing the pivotal role of a well-designed business strategy in achieving sustained growth and success. Examining such success stories provides valuable insights for other companies aiming to optimize their strategic approaches in the ever-evolving business landscape.


